shell script
前言
shell script是在shell中使用的一种脚本语言,是纯文本文档,通过shell去执行脚本。shell script通常可以应用在服务器自动化管理、简单资料的自动化处理、复杂命令单一化和服务器安全稳定性管理等方面。shell script可以帮助我们更好的使用linux系统,但是也存在着局限性。shell script不适合做大量数据处理和运算,shell script属于解释执行类语言,并且运行过程中调用的命令常常会有系统调用和外部库引用,导致占用资源高而执行效率低。我们使用shell script大多数是在管理计算机,对效率要求不高,所以能够成为我们熟练使用linux的有用工具之一。
执行shell script
- 直接执行(注意需要具有rx权限):
- 绝对路径执行:
/home/user/script.sh; - 相对路径路径执行:
./script.sh; - PATH路径执行:脚本位于PATH路径下,
script.sh。
- 绝对路径执行:
- bash程序执行:
bash script_path或者sh script_path。
shell script中的一些默认规则
- 命令的执行是自上而下,从左到右执行的;
- script中指令、参数和选项之间的多个空格会被忽略成一个空格;
- Tab键被视为空白符号,空白行会被忽略;
- 当读到换行时会执行该行的命令,但是当使用\+Enter组合时表示该行命令未结束,表示该行的内容太多,延伸到下一行;
- 注释使用’#’,只能注释一行的内容。
编写程序应该养成较好的习惯
在文档的开头应该做上相应的记录:
- 实现的功能
- 版本
- 作者及其联系方式
- 版权
- 修改记录
- 较为特别的命令使用绝对路径调用
- 需要使用到环境变量的需要先声明和设定
shell script常见的命令
| 命令 | 格式 | 示例 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| echo | echo string | echo ‘hello world’ | 输出一行文本 |
| read | read -p string variable | read -p ‘your name?:’ name | 标准输入中读入数据 |
脚本不同执行方式的差别
- 直接执行脚本:使用
bash script.sh执行脚本,会在当前的bash中使用新的bash环境执行脚本,所有在脚本中产生的变量,会随着脚本执行完毕,bash读到文件EOF退出而消失。 - 使用
source script.sh执行脚本则相反,相当该脚本由当前的bash环境执行,不需要打开新的环境,执行之后bash环境也不会退出,因此脚本中使用的变量还是存在。
shell script的预设变量
/path/to/scriptname opt1 opt2 opt3 ....
$0 $1 $2 $3 ...执行脚本档名可以用$0表示,第一个参数用$1表示、第二个参数用$2表示、第三个参数用$3表示…。
变量偏移
使用shift命令即可将变量进行偏移。
条件判断式
首先注意用到shell中的判断式:shell中的判断式,这里不同的是条件判断式是’if…then’这样的形式。
if…then
简单的条件判断
if [条件判断式]:then
条件满足执行
fi中括号之间可以使用&&和||连接多个条件
例如:
if [条件判断式] && [条件判断式] && [条件判断式]:then
条件满足执行
fi多重复杂条件判断
if [条件判断式]: then
命令
else
命令
fi更复杂的条件判断
if [条件判断式]: then
命令
elif []: then
命令
else
命令
ficase…esac
这种条件判断式的主要格式为:
case $变量名称 in # case式关键词
"第一个变量内容")
命令
;;
"第二个变量内容")
命令
;;
*) # 不包含变量内容
命令
exit 1
;;
esacfunction功能
函数功能使用格式
# 创建函数姿势1
function fname() {
命令
}
# 创建函数姿势2
fname() {
命令
}函数内建变量:在使用调用函数的时候传入参数即可使用函数的参数功能,调用形式:fun par1 par2 ...,在函数内使用预设变量即可获得参数的内容:$1 $2 $3
循环结构
当需要重复执行某个操作时可以使用循环结构实现。
while do done, until do done
while do done
使用方式:
while [条件判断式] # 条件成立循环
do
命令
doneuntil do done
使用方式:
until [条件判断式] # 条件不成立循环
do
命令
donefor…do…done
使用方式:
# for循环姿势1
for var in con1 con2 con3 ...
do
命令
done
# for循环姿势2
for ((初始值;执行条件;执行步骤)) # 和其他语言的for类似,初始值为赋初值,执行条件为判断是否满足循环要求,执行步骤为做完一次循环操作之后所要进行的步骤。
do
命令
donescript的调试和排错
bash [-nvx] script.sh
# 参数说明
# -n 不执行脚本,仅检查是否有语法错误
# -v 首先输出脚本内容再执行
# -x 执行到哪一步将哪一步命令输出示例
script的‘hello word’
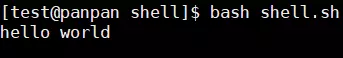
#! /bin/bash # program # this program shows 'hello word' on the screen. # name: shell.sh # history: # 2019/11/11 8315 create the script. echo 'hello world\n' exit 0脚本的第1行为指定脚本的执行程序;
脚本的第2~6行为对该脚本的说明,方便之后对脚本进行修改;
脚本的第7行为输出字符串行;
脚本的第8行表示该脚本正常退出,返回值为0。
运行命令bash shell.sh执行结果:
交互式脚本
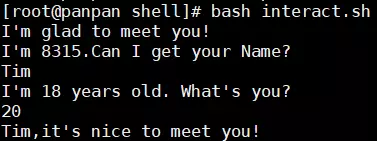
#! /bin/bash # program # get your name and age # name: interact.sh # history # 2019/11/12 8315 create this script echo "I'm glad to meet you!" read -p $'I\'m 8315.Can I get your Name?\n' name read -p $'I\'m 18 years old. What\'s you?\n' age echo "${name},it's nice to meet you!" exit 0命令的前6行为该脚本的一些基本信息,便于以后修改
第8行的字符串前面加’$’是为了在字符串中能使用转义字符.
第10行的’${name}’表示使用name变量的内容
创建带日期的文件
#! /bin/bash # program # use date as the filename to create file. Ps:filename_20191112 # name: createfile.sh # history: # 2019/11/12 8315 create this script echo "I will use 'touch' command to create file." read -p 'Please enter filename:' filename # 提示输入 # 判断文件名是否为空 if [[ -z "$filename" ]] then echo 'empty filename!' exit 1 fi sdate=$(date +%Y%m%d) filename=${filename}'_'"$sdate" # 创建文件 touch "$filename" exit 0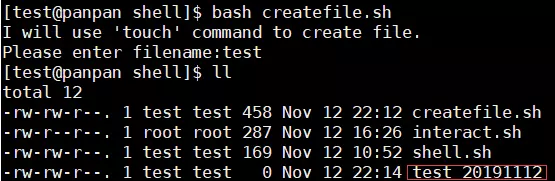
文件判断之后再讲解。简单数值运算
创建一个脚本使得两数相乘#! /bin/bash # program # Input two integers. The program will get the product of two nums. # name: mutiply.sh # history: # 2019/11/13 8315 create this script. echo 'Input two integers. You will get the product of two nums.' read -p 'the first integer:' firstnum read -p 'the second integer:' secondnum echo -e "compute by \$(()):" echo $((${firstnum}*${secondnum})) echo -e "\ncompute by declare:" declare -i result=${firstnum}*${secondnum} echo "$result" echo -e "\ncompute by bc:" echo ${firstnum}*${secondnum} | bc exit 0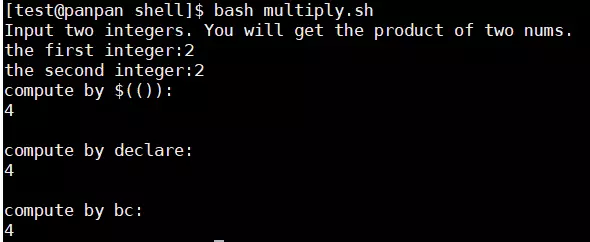
判断路径是否存在的脚本
#! /bin/bash # program # determine whether the path exsits # name: determine,sh # history: # 2019/11/15 8315 create the script read -p 'please input the determined path:' dpath ( [ -z ${dpath} ] && echo ' erro:input empty string' ) || ( [ -e ${dpath} ] && echo 'path exists' || echo 'path not exsits' ) 判断式相关:shell中的判断式
使用脚本中的预设变量
#! /bin/bash # program # use 3 preset parameter # name: presetparameter.sh # history: # 2019/11/15 8315 create this script echo 'this script called by:'${0} echo 'three parameters is:'${1} ${2} ${3} exit 0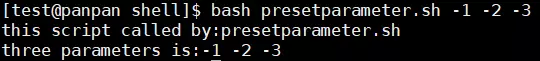
预设变量偏移
#! /bin/bash # program # shift the preset parameters # name: shift preset parameters # history: # 2019/11/15 8315 create this script echo "Total parameters num is:$#" echo "Your whole parameters is:$@" # first shift echo 'first shift' shift echo "Total parameters num is:$#" echo "Your whole parameters is:$@" # second shift echo 'second shift' shift echo "Total parameters num is:$#" echo "Your whole parameters is:$@" # third shift echo 'third shift' shift echo "Total parameters num is:$#" echo "Your whole parameters is:$@" exit 0“$#”表示预设变量总数,”$@”表示所有变量
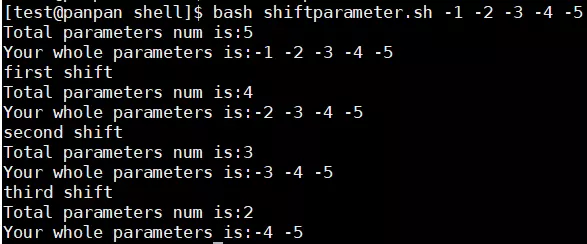
通过预设变量给函数传入参数
函数传入多个参数,最多打印3个参数内容
#! /bin/bash # program # print parameters of function # name: funparameter.sh # history: # 2019/11/16 8315 create the script. printpara() { case ${#} in "0") echo "no parameter!" ;; "1") echo "only one parameter:$1" ;; "2") echo "two parameters is:$1 $2" ;; *) echo "three or more parameters, but I print the first three parameters: $1 $2 $3" ;; esac } printpara 1 2 3 4 5 6 exit 0
通过/etc/passwd提取所有的用户
#! /bin/bash # program # get all users from /etc/passwd # name: getusers.sh # history: # 2019/11/16 8315 create the script. users=$(cat /etc/passwd | grep '/bin/bash' | cut -d ':' -f1) # grep是为了过滤掉不需要的部分 # loop for printing all users echo "User list:" for username in ${users} do echo ${username} done exit 0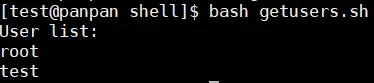
参考资料
鸟叔的linux私房菜-第十三章:< http://linux.vbird.org/linux_basic/0340bashshell-scripts.php >
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 qinzhtao@163.com
文章标题:shell script
文章字数:2.2k
本文作者:捌叁壹伍
发布时间:2019-11-11, 16:11:51
最后更新:2019-11-17, 17:38:13
原始链接:http://qzt8315.github.io/2019/11/11/shell-script/版权声明: "署名-非商用-相同方式共享 4.0" 转载请保留原文链接及作者。

